topRik experts give advice on choosing and installing a marine inverter on a yacht. All recommendations have been tested in practice. We have the opportunity to test various types of inverters at sea - on different-sized yachts and catamarans of our SimpleSail fleet with various options for electrical equipment and ship electrical system layouts.
topRik marketplace offers only proven multifunctional marine inverters from the best manufacturers of marine electrical equipment – Victron Energy, Mastervolt and others. Choose from the options offered or contact our experts for a free consultation directly through the contacts listed on this page.
How Does an Inverter Work and What Is It for on a Yacht?
The inverter converts direct voltage of 12 or 24 V into alternating voltage of 220 V and serves as an excellent alternative to the generator.
For most small boats and yachts, a diesel generator is an unaffordable luxury. Its cost is high, and the lack of space on the boat and the noise it produces during operation are additional obstacles to organizing an AC system on board.
The inverter increases comfort on board. It allows you to enjoy peace and quiet at anchor, saves money and has a minimum of disadvantages. Most owners of boats and sailing yachts equipped with inverters will agree with this.
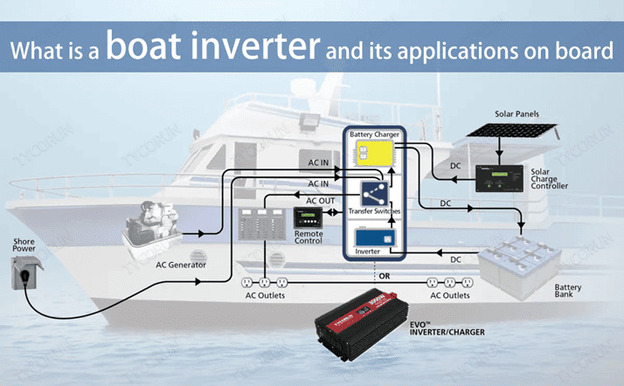
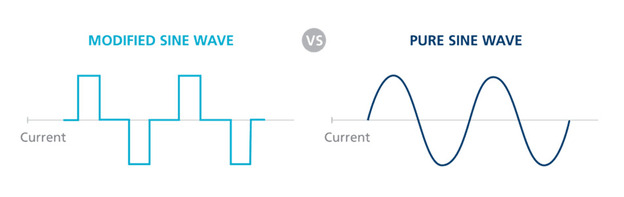
The inverter's operating algorithm depends on its type. There are two types of inverters. The output voltage of the first group is the same as in the city network and has the form of a pure sine wave.
In the second group of devices, the voltage looks like a stepped square wave, so such models are called modified sine wave inverters.
Types and Features of Marine Inverters
The inverter operates on the principle of using high-speed switching transistors. Depending on the design, type or model of the inverter, specific technical details and features may vary, but the general steps of the conversion are as follows.
The controller controls two groups of transistors and opens them in turn. Due to this, the voltage on the load periodically changes polarity, i.e. from constant to alternating. The frequency of the alternating voltage obtained in this way is determined by the speed of switching the transistors, and its value is determined by the voltage of the source. If the output voltage needs to be increased, a transformer is added to the circuit , and the transistors are connected to its primary winding. The voltage from the secondary winding is fed to the output.
The alternating voltage obtained in this way has the form of a square wave and is not suitable for powering most devices. Therefore, in sinusoidal inverters, the controller turns the transistors on and off not once, but many times during each half-period. As a result, the output voltage takes the form of repeating pulses that follow with the same frequency but have different durations. The pulse width changes over time according to a sinusoidal law, so the average voltage over the switching period takes the form of a pure sinusoid.
After the conversion is complete, the alternating voltage is filtered, cleared of high-frequency components and sent to the output. Safe operation of connected consumers is ensured by the inverter's protection against short circuits, overloads, overheating and other emergency situations.
Pure sine wave inverters are universal. Unlike modified wave models, they can easily power both resistive loads (incandescent lamps, toasters, electric kettles) and any household or office equipment.
This means that the washing machines, dishwashers, complex coffee makers, televisions, stereo systems, microwave ovens, etc., as well as AC motors on your yacht require sine wave voltage.
The alternating voltage at the inverter output is obtained using electronic keys that open and close many times per second. If the keys operate several tens or hundreds of thousands of times, then the inverter is called high-frequency. And if the switching frequency is equal to the frequency of the output alternating voltage, then it is linear.
Linear and high-frequency devices differ in weight and size. A 2000 W linear inverter with both pure and modified sine waves weighs about 20 kg. A high-frequency model of the same power weighs half as much and takes up one-third the volume of a linear device.
High frequency pure sine wave inverters are often less efficient than modified wave models and draw more current when not in use. Since the battery charge is limited, the inverter's own consumption when left in standby mode for a long time will greatly affect the condition of the batteries on the boat or yacht. Therefore, the inverter should always be turned off when you are not on board.
The neutral conductor of an AC circuit is grounded only at the voltage source. This means that before starting work, an inverter installed on board a boat or yacht must connect the neutral to its own ground wire, and after the vessel is connected to the shore power grid or another source of AC voltage, it must disconnect them. All marine inverters do this automatically, but shore inverters do not. Therefore, before buying an inverter for a boat or yacht, make sure that you are buying a model specifically designed for marine use.
Can an Inverter Also Work as a Charger?
An inverter combined with a charger is a device capable of converting electrical energy in two directions. In inverter mode, it receives alternating voltage from the battery's direct voltage, and in charger mode, on the contrary, it receives direct voltage from alternating voltage.

The frequency and amplitude of the alternating voltage generated by the inverter do not differ from the characteristics of a stationary electrical network, so household or office equipment connected to it can operate even where there is no access to a regular outlet.
How to Charge a Battery with an Inverter
In addition to the inverter, the combined models include an automatic power supply switch (ATS – Automatic Transfer Switch) and a battery charger. ATS monitors the state of the AC input and, as soon as it detects alternating voltage on it, automatically, in a split second, switches the inverter-charger from the inversion mode to the mains power mode and simultaneously turns on the charger. Switching occurs so quickly that the equipment operating at that moment does not have time to “notice” anything and continues to perform its functions without interruption.
The charger's available algorithms are suitable for gel, wet-acid, AGM and LiFePO4 batteries. Some models allow the user to create a custom charging profile to use when none of the preset modes are suitable for the battery.
Modern models of inverters with battery charging are equipped with protection against overload, high/low voltage, short circuit, overheating and therefore ensure safe operation of both the battery and the on-board AC system. Models with Bluetooth allow the user to control the operation of the device or configure it from an application on a mobile phone.
An inverter with a charger is widely used in autonomous electrical systems that do not have constant access to grid electricity. They are installed in motorhomes, campers, boats, motor and sailing yachts, houseboats, mobile offices, mobile laboratories and other special-purpose vehicles in which AC equipment is installed, as well as in autonomous electrical systems based on solar energy.
How to Choose the Right Inverter for a Specific Yacht and Install It Correctly
Until recently, the electrical system of a sailing or motor yacht with alternating voltage on board was based on a diesel generator. And although a small inverter was sometimes installed simultaneously to power low-power devices, the generator still had to regularly work for a long time, accompanying its work with irritating noise and exhaust gases.

In a hybrid electric system, the inverter and generator switch places. Most of the time, the on-board equipment is powered by an inverter with a capacity of 3, 5 or 8 kW. And as soon as the battery charge drops to a pre-set limit, the inverter stops converting direct voltage to alternating voltage, automatically starts the generator and switches to charger mode. In this case, the power used to charge the battery can change depending on the load in the on-board network. Thanks to this, the generator is compact and only works for a short period of time.
On small boats and yachts, an inverter allows the use of AC devices without having a gasoline or diesel generator:
- Yachts 8-10 meters long are most often used for short trips on the sea or inland waters. On such trips, basic comfort is important - warm water from the tap, a small shower, heating, a compact kitchen with an electric stove and refrigerator, a coffee machine. Therefore, the boat's electrical system consists of a lithium battery, a sine-wave inverter that converts its voltage to 220 V, an AC-DC charger and equipment for connecting the boat to shore power. Additionally, a solar panel with a capacity of 100 or 200 W can be installed.
- Yachts 9-12 meters long have higher demands for comfort. In addition to the equipment listed above, vessels of this size often have an air conditioner, dishwasher, and other energy-intensive devices. The necessary energy for household appliances is provided by a lithium-iron-phosphate battery and an inverter with a capacity of 2 or 3 kW. The charger built into the inverter charges the batteries from the shore network, and the DC-DC charger charges from the engine generator. Without compromising comfort, the weight of a boat equipped in this way can be reduced by 500 kg, but despite this, there is always enough energy on board.
- Yachts 11-14 meters long: the advanced electrical system provides more comfort on board, and the diesel generator makes the vessel completely energy independent. The inverter combined with the charger is capable of both powering AC devices and charging the battery. Power Assist function allows the inverter to work simultaneously with the generator or shore power, providing onboard equipment with additional power. Solar panels charge the batteries throughout the day, and the DC-DC charger quickly restores their condition while the boat is moving.
That is, for a yacht that does not have equipment that consumes 220 V, one 2 kW inverter is enough. We do not recommend installing a lower-power inverter on a boat based on possible additional electrical equipment. For a 50-foot catamaran, which usually has an induction cooker, washing machine, dishwasher, electric kettle, microwave oven, etc., two 3 kW or more powerful inverters should be installed in parallel, taking into account all the available equipment.
It remains to add that even marine inverters equipped with protective covers and having a high protection class should be mounted in a place where water will not get on it. An inverter is a complex electronic device, the elements of which are made of different metals. Therefore, moisture getting inside the case creates an ideal situation for the development of electrochemical corrosion. All the components necessary for this - water, electricity and dissimilar metals - are present in one place. To prevent corrosion, the inverter must be installed in a dry place, protected from splashes or condensation.
The inverter's performance is temperature dependent. Therefore, a device operating at full power must be well cooled by a flow of cold air that will freely remove heat from the inverter.
It is better to install inverters with a charger function near the batteries.

To avoid voltage drop in the cable coming from the battery, its cross-section must match the current consumed by the inverter. The peak current of a powerful device in a 12-volt electrical system reaches 1000 A. This means that such an inverter will have to be connected to the batteries with a 4/0 AWG (110 mm2) cable, even if the device is located at a distance of 1.5-3 meters from the battery.
It is difficult and inconvenient to lay cables of large cross-section. Therefore, you should not try to connect them directly to the terminals of the battery. Especially if, in addition to the inverter, other powerful consumers are already connected to it - the main panel, an additional generator or a winch. Instead, it is better to use positive and negative buses designed for the appropriate current. And then connect them to the battery terminals with a cable of large cross-section. Additionally, the inverter body is connected to a common grounding point. The cross-section of the grounding cable should be one size lower than the main negative conductor.
We have already said that cable losses will be lower if the inverter is located near the battery. However, since batteries can emit corrosive and explosive vapors, the inverter must be located outside the battery compartment.
In the event of a short circuit, the battery is capable of generating a significant current. To protect against its destructive effects, a circuit breaker or a slow-blow fuse is installed on the cable leading to the inverter as close as possible to the battery terminal.
Before connecting or repairing the inverter, make sure that the unit is disconnected from the batteries. In standby mode, many inverters do not show any voltage on the multimeter . However, as soon as a load appears, for example, simply touching the AC output terminals, the inverter turns on and operates at full power.
If the inverter or the battery it runs on cannot handle certain loads, the corresponding equipment is connected to an AC panel that is not connected to the inverter. An independent charger is also connected to the same panel. The circuit avoids a situation where the charger runs on the inverter and simultaneously charges its batteries. Such a loop will, at best, waste battery power, and, at worst, can damage the inverter and charger.
All inverters for marine use in AC mode must connect the neutral to its own grounding circuit. This is consistent with the requirement to ground the neutral at the power source. However, this connection must be broken when another AC source is connected, so as not to ground the neutral anywhere other than the power source. As we mentioned above, all marine inverters do this automatically, but land-based models do not. So again, it is important to install an inverter specifically designed for marine use on your yacht.
Selection of Marine Inverters at the topRik Marketplace
We have selected for you multifunctional marine inverters for installation on small vessels of various sizes and designs. The peculiarity of the models from Victron Energy, a recognized leader in this area, is that most of them can be used for various objects, including professional marine, yacht, transport and land-based autonomous installations. Good examples of this are inverter series like MultiPlus, MultiGrid, MultiPlus-II, Quattro, Quattro-II, EasySolar, EasyPlus.
Victron Energy hybrid inverters feature high peak power, pure sine wave, optimized battery charging algorithm, as well as protection against short circuit, overload and overheating.
Victron Energy inverters can operate in parallel, forming a single-phase or three-phase network. Additional accessories allow remote control of the solar power plant, changing system settings and collecting statistics. Some models are equipped with two inputs for different AC sources (for example, for an external network and a diesel generator) and two outputs (for critical and non-critical loads).
MultiPlus and MultiPlus-II Series Inverters
This transformer inverter charger in a robust aluminum case has 8 modifications, which are equipped with one AC input and two AC outputs. Models with a capacity of 3,000 VA are available with an operating voltage of 12, 24 or 48 V. Inverters with a capacity of 5,000 VA can be with a voltage of 24 or 48 V.
The second generation of the legendary inverter combines the best features of the MultiPlus and MultiGrid models, while having a more compact body and an affordable price. As an option, it is possible to use an external current sensor to implement the PowerControl and PowerAssist functions.
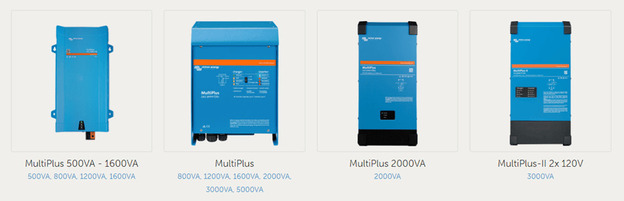
Quattro Series Inverters
Inverter charger Victron Energy Quattro has 9 modifications with a capacity from 3 to 15 kVA. The model features two AC inputs with the ability to automatically switch between them. There are also two AC outputs: one of them works constantly and is designed for critical loads, and the second - only when there is alternating current at one of the Quattro inputs.
EasyPlus Series Inverters
Multifunctional system consisting of a sine wave inverter, high-efficiency charger and high-speed switching relay. Four AC outputs with built-in circuit breakers and RCD (residual current device). PowerControl and PowerAssist functions – limiting consumption and adding power at the input. Operation in both 3-phase and parallel configurations is allowed.
EasySolar, EasySolar II Inverter Series
To work with photovoltaic modules, early models of Victron Energy inverters require charge controllers. When the external network is disconnected, the inverter's transfer key instantly switches to operation from storage batteries, ensuring uninterruptible power supply to consumers.

EasySolar and EasySolar II are a nice exception as they combine an MPPT solar controller, inverter/charger and AC distribution system into one housing.
Inverters of these series are equipped with a control panel with a color display and have unique functions:
- battery charging priority using MPPT charge controller;
- AC distribution;
- unique PowerAssist technology;
- unique software for solar applications;
- Internet connection, which allows for remote monitoring and control.
Common Features of Victron Energy Inverters
Almost all of the listed models have the Power Control function. What does it mean? Any sailor knows: the less time the generator runs, the higher the efficiency of the electrical system. You’ll achieve the minimum generator operating time if several onboard devices, including the AC-DC charger, work simultaneously, and not in turn.
The inverters combined with chargers presented in our marketplace help to achieve this. The Power Control module constantly monitors the generator's output current and automatically regulates the power used to charge the batteries so that the total generator load remains within pre-set limits.
If the combined inverter with Power Control function reduces the battery charging current to avoid overloading the generator or shore power when the electrical load on board increases to the maximum value, then devices with the Power Assist function is capable of operating simultaneously with an external AC voltage source.
The listed models are equipped with these two functions. For example, the MultiPlus-II 12/3000/120-32 is a very powerful inverter. Therefore, it will be able to consume a lot of power from the grid, but it is possible to program the current consumption limit, and you can do this on each AC input. The model takes into account other AC loads and uses everything possible to replenish the battery capacity, thereby preventing increased load on the generator or the electrical grid.
Power Assist feature takes Power Control further by allowing the MultiPlus-II 48/3000/35-35 to supplement the grid power supply. Where more power is only needed for a limited period of time, the inverter will ensure that grid or generator power is compensated for by battery power. When the load decreases, the excess power is used to recharge the batteries.
The same inverter can be used both in electrical systems on stationary objects and in conventional or marine transport, as well as in networks with connected solar modules and other alternative energy installations.
For detailed free consultation – contact our experts, experienced sailors, who will help you choose an inverter or inverters that will be effective for a vessel with specific characteristics. All contacts are listed on this page.








